Effective Cybersecurity Strategies for Healthcare Institutions
Recent statements by the United Nations Surgeon General to the Security Council have raised concerns about the current state of cybersecurity in hospitals. He stated that ransomware attacks against hospitals and health systems could be “a matter of life and death” and pose a serious threat to international security. Several delegates called for international cooperation to address one of today’s most destructive cyber threats. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach 2024 Report, the healthcare industry has topped the list of the most expensive industries to recover from a data breach for 14 consecutive years, with an average cost of $9.77 million. These are signs that hospitals need to implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy and continually improve the security awareness and technical skills of their staff to meet these ever-emerging challenges.
Major Cyber Threats to Modern Hospitals
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware in which an attacker blocks access to a device and its stored data by encrypting files and then demands a ransom from the organization in exchange for decryption. Ransomware attacks in healthcare are one of the most common cyberattacks that not only affect the normal operations of hospitals but can also jeopardize patient safety. Ransomware attacks in healthcare rise from 60% in 2023 to 67% in 2024. And according to Microsoft’s latest annual Digital Defense Report, July 2023 through June 2024 (Microsoft fiscal year 2024), 389 healthcare organizations in the U.S. suffered from ransomware attacks that resulted in network shutdowns, systems going offline, delays in critical medical procedures, and rescheduling of appointments, among other consequences.

Data Breach
Healthcare data systems often contain a large amount of sensitive information within them, including patients’ personal health information (PHI), financial data, medical records, and more. Once this data is compromised, it can lead to serious privacy violations and identity theft.
There is no denying that digital record-keeping has many advantages over traditional paper-based methods of retention. While technology has evolved, hospitals have reduced the potential for system intrusion, unauthorized data access, and disclosure by adopting and more accurately tracking electronic devices, as well as more widespread use of data encryption. However, the ever-increasing number of hacking incidents has led to a continued upward trend in the number of data breaches occurring over the past 14 years. And we can see that the number of data breaches is not only increasing but getting worse.
Social Engineering Attack
Attacks in which the attacker obtains sensitive information through deception, such as phishing and phone impersonation, may also pose as a trusted entity to trick hospital staff into providing login credentials or other sensitive data. Technically speaking, social engineering is not an attack technique, it is more of a “trick,” and because it focuses on people’s psychology and behavior, it has a very high success rate—after all, everyone can make a mistake, and people are the most vulnerable part of security measures. Although the victim will usually doubt the authenticity of the email or phone call, because the attacker carefully designed a complete attack process, so often people will make the wrong judgment and disposition.
Impact and Consequences of Cybersecurity Threats on Hospitals
Data Breach
Internal healthcare systems contain a lot of sensitive personal information, and any inappropriate access to these systems puts the privacy of patients and healthcare workers at risk.
Service disruptions
Hospital cyberattacks can cause emergency systems to crash, affecting the timely treatment of emergency patients, as well as compromising appointment systems and exam equipment, forcing appointments and exams to be postponed and affecting patients’ treatment plans.
Financial losses
Ransom payments and post-data recovery and maintenance costs.
Reputational damage
A sustained cybersecurity incident can diminish the public’s perception of the hospital’s credibility, and relationships between some partners may be impacted.
Legal Liability
Hospitals can face stiff fines and lawsuits for data breaches and are required to comply with relevant data protection regulations; for example, in Germany, healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA, GDPR, Nis2, and the German Patient Data Protection Act (PSDG), and any breaches can lead to lengthy compliance reviews and corrective actions.
Why Hospitals Are High-Frequency Targets for Cyberattacks
Massive amounts of sensitive data
For hackers, hospital systems store large amounts of sensitive information of great value, including patients’ names, addresses, social security numbers, medical history, diagnostic information (HPI), and more. Whether it’s obtained illegally and sold on the dark web or ransomed to hospitals for a high ransom, the healthcare industry is increasingly becoming a target for attack.
Aging IT systems
Hospital IT systems handle large amounts of sensitive information, yet due to a lack of up-to-date security patches and updates, older IT systems are susceptible to cyberattacks and virus infections. In addition, these old systems are not compatible with modern and emerging cybersecurity tools or technologies.
IT staff challenge and inadequate training
Unlike Internet companies or manufacturing industries with specialized IT teams, hospitals typically lack specialized, qualified IT talent, making it difficult to respond to increasingly complex cybersecurity threats. And with hospital staff scrambling to save lives, budget, resource, and time constraints mean that all healthcare professionals are unlikely to be well versed in cybersecurity best practices. As a result, awareness and training on cybersecurity are not sufficient, and phishing emails may be accessed inadvertently or compromised by malware, which is a major reason why hospitals are becoming targets of cyberattacks.
Unwilling compromises fuel attacks on hospitals
When facing cyber extortion, some hospitals choose to pay the ransom to recover their systems and data as soon as possible. Indeed, this practice can solve the problem temporarily, but it neglects the long-term network security construction, and the system still has vulnerabilities and risks. Most importantly, this practice sends a signal to hackers that “ransom works,” which undoubtedly encourages the emergence of more similar attacks. And hospitals may also be classified as ‘soft targets’ by hackers after a compromise, thus becoming one of the main targets for future attacks.
Medical Device Networking
Today’s vast network of connected medical devices significantly improves the efficiency and quality of healthcare delivery, as these devices not only monitor a patient’s health status in real time but can also be controlled and adjusted remotely. Yet this connectivity also poses significant challenges. For example, patient information stored on medical devices can be accessed without authorization, and these devices can be remotely accessed and controlled by attackers who can even tamper with the transmitted data.
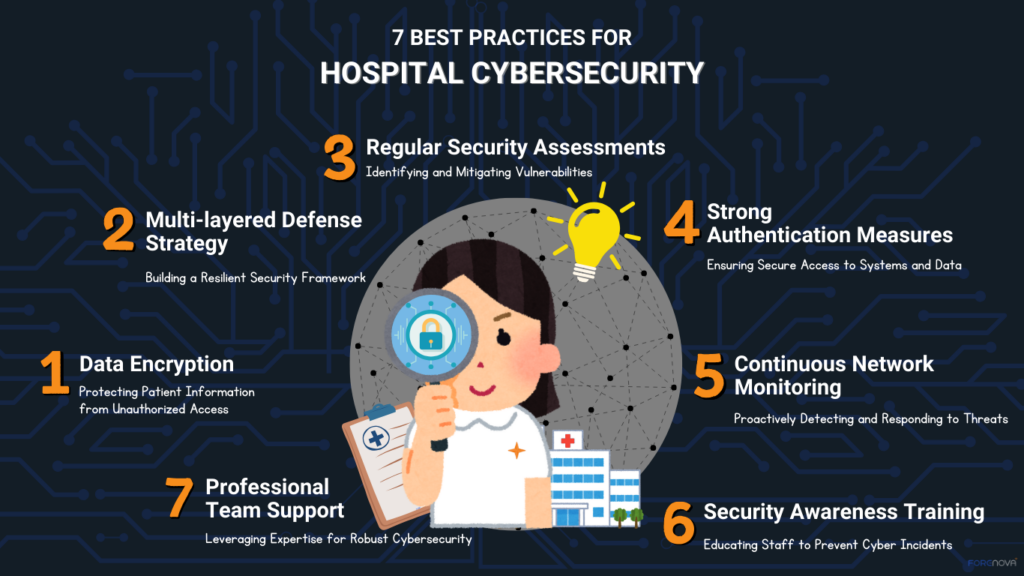
Best Practices for Hospital Cybersecurity
- Data Encryption: To better protect against data interception and tampering during transmission, hospitals should ensure that all data is encrypted during transmission.
- Multi-layered defense strategy: Hospitals should establish a defense-in-depth strategy that includes the use of multi-layered security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to comprehensively protect hospital network security.
- Regular Security Assessments: Hospitals should conduct regular security assessments to identify and fix vulnerabilities and potential risks in their networks.
- Strong Authentication Measures: Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to improve system security by ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information.
- Continuous Network Monitoring: Continuously monitors network traffic, detects and responds to suspicious activity in real time, ensuring that security threats are detected and addressed in a timely manner.
- Security Awareness Training: Hospitals should conduct regular security awareness training for their staff to prevent security accidents due to human error and to improve the overall security preparedness.
- Professional team support: Hospitals should remain sensitive to emerging technologies and introduce new security tools and solutions like NovaMDR in a timely manner to continuously improve their network protection capabilities.
Cybersecurity is not static but needs to be constantly improved and updated to address the changing threat landscape. ForeNova team has a wealth of experience and expertise in the field of cybersecurity, and we are able to customize cybersecurity strategies that are best suited to the specific needs of different hospitals. And NovaMDR can provide healthcare organizations with 7×24 comprehensive cybersecurity solutions and compliance guidance to ensure that hospitals comply with various regulations while protecting sensitive data and systems.
Contact our team of professionals today and start protecting your organization from cyber threats today.






